This assignment is about using OpenGL 2D transformations as described in the textbook in Sections 5.1, 5.2 and 5.4. This assignment has three parts. Each part is an OpenGL program that uses a simple model and a number of transformations of that model to construct a complex scene.
Download this zip file. In the zip file you will find a skeleton OpenGL program called problem1.c and several image files that show sample results of the completed program. Your program should read an integer n off of the command line and then draw n equilateral triangles placed around the circumference of the unit circle. In the file problem1.c a model for an equilateral triangle is already defined. Your program should use OpenGL rotation, scaling, and translation transformations to place n instances of the model around the circumference of the circle. Here is what the result should look like when n = 8.
.png)
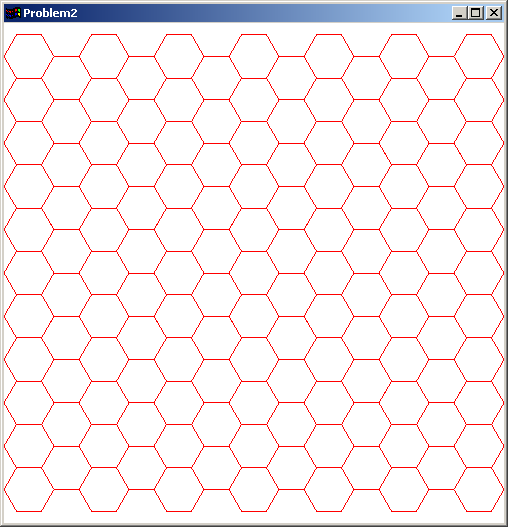
For the second problem, write an OpenGL program called problem2.c that draws the following hexagonal tiling. Your program should define a model that is a single hexagon inscribed in the unit circle. Your program should use OpenGL translation transformations to place the model in the scene so as to create the tiling. This image is an orthogonal projection of the (x,y)-plane with x between -10 and 10 and with y between -10 and 10.
For the third problem, there is a demo program problem3-demo.exe that lets you see what your program should do and an outline of the program in the file problem3.c. The program draws four scenes in four square viewports. Each scene is made up of 20 squares and in each scene the 20 squares are somehow distributed around a circle. The basic square used in every scene is a model that is included in the outline program problem3.c. The scene in the first viewport just rotates this model around the origin. The slider is used to determine a maximum rotation of the model (the maximum rotation is sliderValue*360 degrees). The scene in the second viewport translates the model square to have one corner at the origin, and then it rotates this square (20 times) around this corner. The third viewport scales the square to have side length 1, and then it translates the square (20 times) so that its center is on the unit circle (in the demo program, the unit circle is drawn in green to help you see it; your final program doesn't need to show this green circle). The fourth viewport is similar to the third one, but the model is rotated clockwise by the amount sliderValue*360 degrees before it is translated (20 times) to a place on the unit circle.
Turn in a zip file called CS455Hw4Surname.zip containing your versions of the three C programs problem1.c, problem2.c, and problem3.c.
This assignment is due Wednesday, March 2.